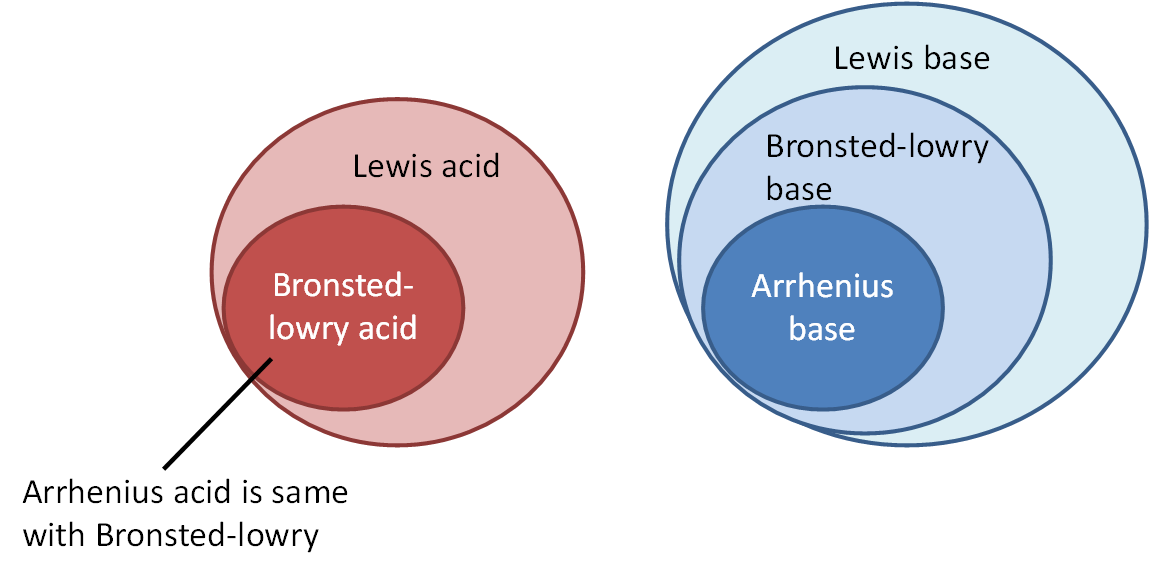
8.1a Various theories about acids and bases
There are three theories about acids and bases: Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis.
Note: SL only needs to know the first two (no Lewis), HL all three
Arrhenius is the earliest theory. Essentially it only identifies strong acids and bases such as HCl, H2SO4, NaOH, KOH...
The theory says acids give out H+ while bases give out OH-
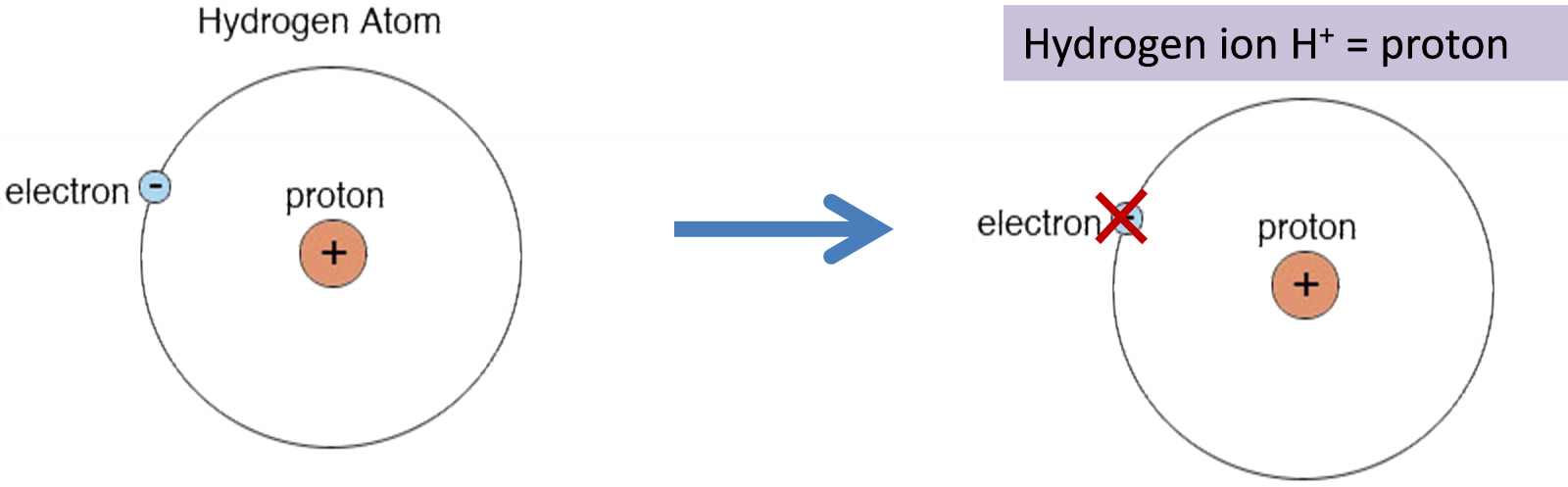
Bronsted-Lowry focuses on the proton.
The proton
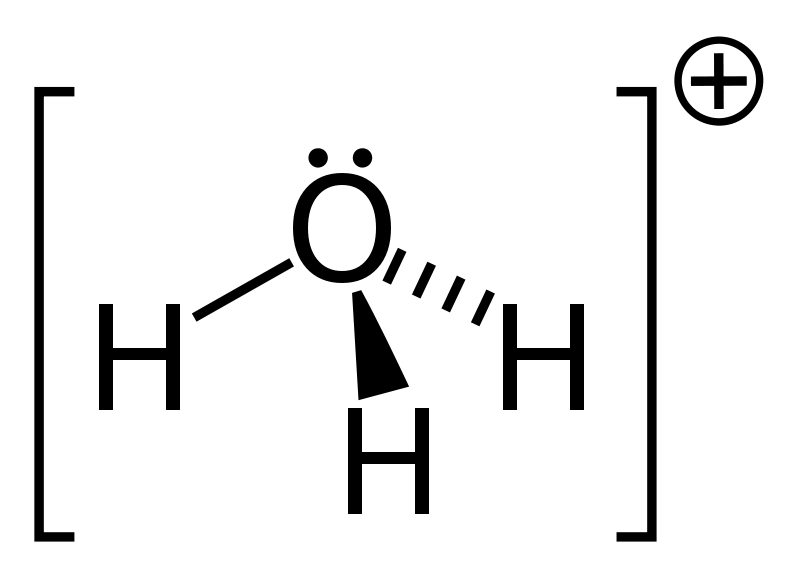
A proton can also be shown as Hydronium H3O+ = protonated water
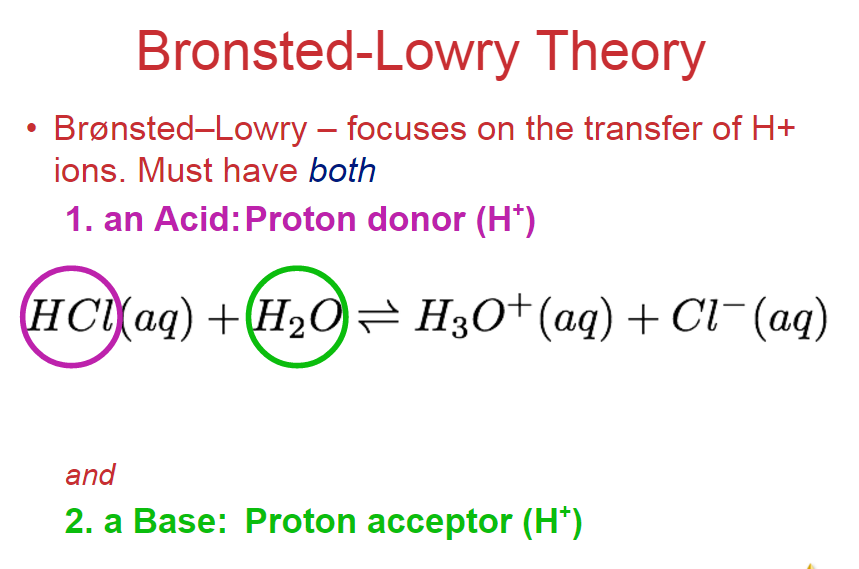
Bronsted-Lowry acid and base pair
What is the difference between the terms amphoteric and amphiprotic?
An amphiprotic substance is one which can both donate hydrogen ions (protons) and also accept them.
Amphoteric means that they have reactions as both acids and bases.
So?
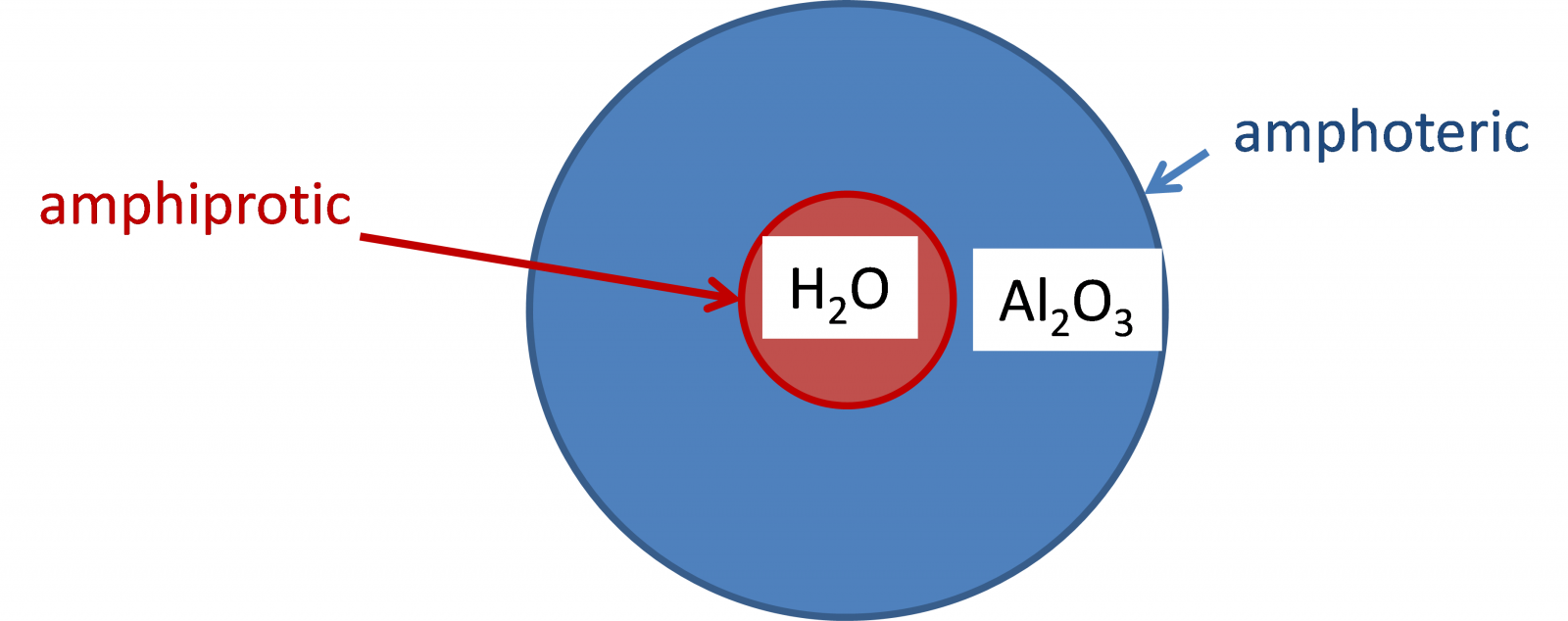
Note that Aluminium oxide is both acid and base (Unit periodicity) but it doesn’t donate proton so it can’t be amphiprotic
Quick review:
- Which oxides are amphoteric?
- What is the equation for Na2O in water?
- What is the equation for P4O10 in water?









