4.3a Covalent structures
Lewis (electron dot) structures show the electron domains in the valence shell
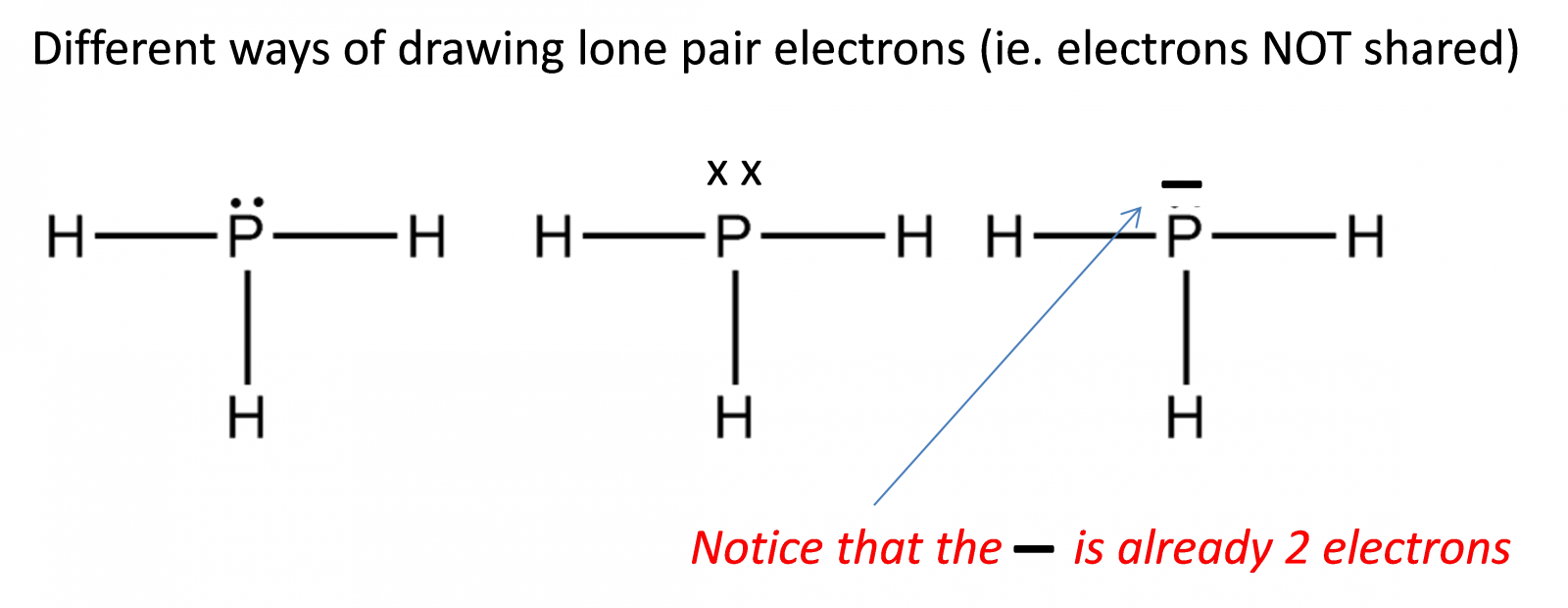
- Lewis (electron dot) structures show all the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule or polyatomic ion. Four steps to draw Lewis structure.
- 1. Calculate the total number of valence electrons. Plus 1 electron for each (-) charge and minus 1 electron for each (+) charge.
- 2. Place the element with the least number in the middle, surrounded by the other. Ex: CH4 then put C in the middle, surrounded by 4 H
- 3. Predict the number of covalent bonds using the octet rule (except for H only needs 2 and B only needs 6).
- 4. Count the number of electrons (2 for each bond) and put in the dots for electrons to reach the total number from step 1.
- The octet rule refers to the fact that most atoms form a stable arrangement with eight electrons in their outer shell.
- Exceptions to the octet rule include:
less than an octet – BeCl2, BF3 (central atom very small)
expanded octet – PCl5, SF6 (central atom from third period or beyond).
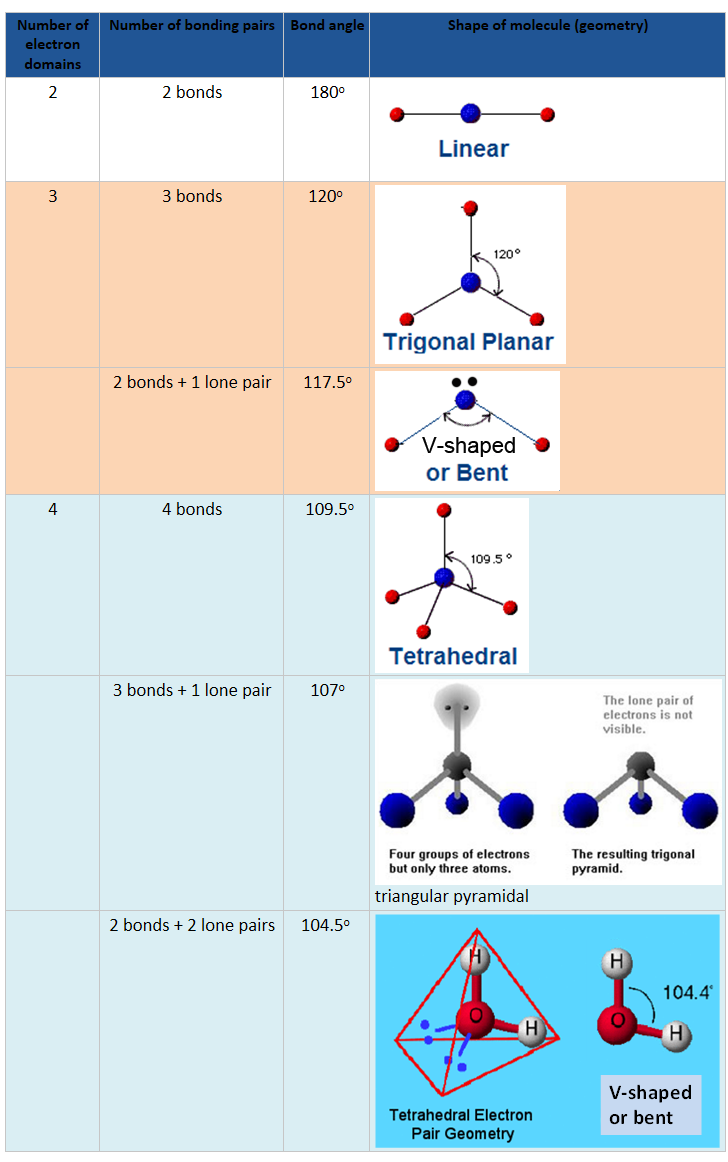
VSEPR theory: are used to predict shape of the molecule.
Remember: 1 lone pair = minus 2.5o from the angle
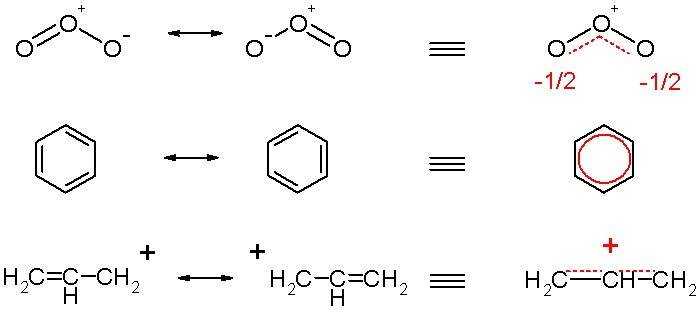
Resonance structures occur when there is more than one possible position for a double bond.
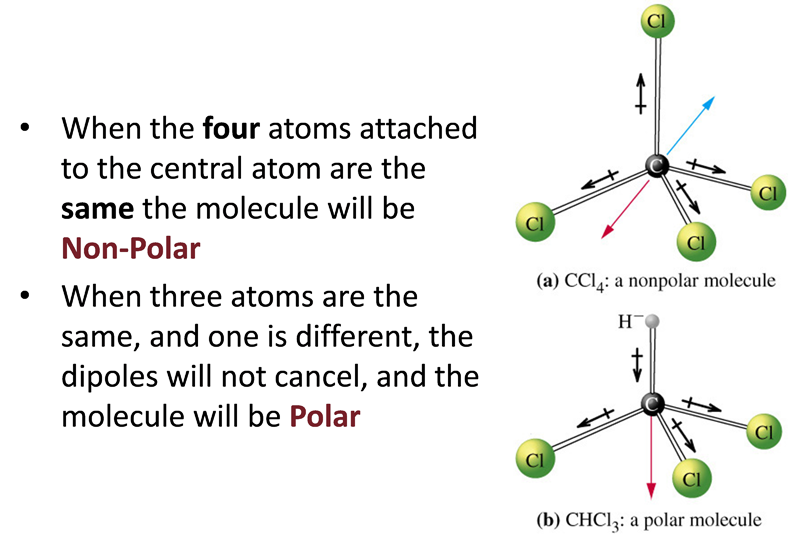
The polarity of a molecule depends on:
i the polarities of its bonds
ii its molecular shape – whether cancellation occurs between the polar bonds.
Be careful of the lone paired electrons!!!
Coordinate bonds (same as Dative bond) form when both the shared electrons originate from the same atom.









