4.5 Metallic bonding
Metallic bonds involve a lattice of cations with delocalized electrons (sea of electrons).
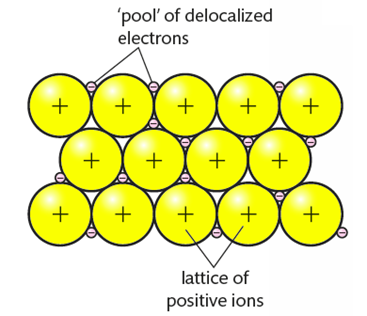
- Metal atoms are held together by the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive ions and delocalized electrons.
- The strength of the metallic bond increases with the charge on the cation and decreases with the radius of the ion.
- The properties of metals – electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, ductility - are a result of the delocalized electrons.
- Alloys form as a result of the non-directional bonding in metals and often have enhanced properties.
What is the big deal about directional and non-directional bonding?
- Directional is that atoms prefer specific orientations in space relative to one another = molecules have definite shapes
- Non-directional is when charge are uniform in all direction = no definite shapes
|
Direction or non-directional |
Consequence |
|
|
Covalent bond/ coordinate bond |
directional |
Definite shapes (VSEPR) |
|
Ionic bond |
Non-directional, lattice structure |
If you hammer a lattice structure, the (+) and (-) ions mis-alined and the crystal breaks → ionic compound are fragile |
|
Metallic bond |
Non-directional, uniformal structure |
If you hammer a metallic bond structure, the positive ions just slide over → pure metal is malleable (bendable) |
|
Alloy (mixture or some metallic bond) |
Non-directional, less uniformal structure (because of the added atoms of different size - see video below) |
Alloy is a mixture of different size atoms of different elements, at least one of them is metal atoms. This mixture makes the metal harder because it is no longer as uniformal as pure metal |









