7.1c Constant and quotient
Same same… but different
Equilibrium constant Kc
![Machine generated alternative text:H2(g)+I2(g)2HI(g)if we take the equilibrium concentrations and process them in the following way:: = coefficient ofHl in tue reaction équation[Fll]qmFH it : 1 = coefficient of H2 in the reaction equation. 2kqmL2icqm . . . .1• 9Pc ° ! in the reaction euatio](http://ibmole.com/upload/files/images/Topic%207/7_1_4_1.png)
Equilibrium quotient Q
![Machine generated alternative text:H2(g)+ Í2(g) 2H1(g)Ifvetake the instantaneous concentrations and process them in the following way:: = coefficient of HI in ti’e reaction equation[HI]2[H2 j 2Ì : 1 = coefficient of H2 in the reaction equation1 9 !z in the reaction equatio](http://ibmole.com/upload/files/images/Topic%207/7_1_4_2.png)
So what?
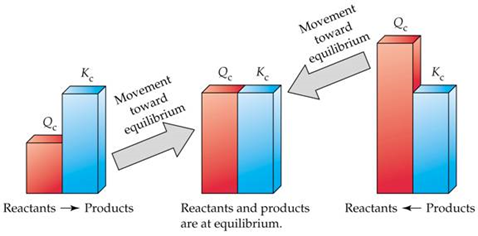
What about the inverse reaction?
What does it mean to have large Kc? Small Kc?
Teacher's note:
- Use
Co(H2O)6 2+ + 4 Cl- + heat equilibrium <--> CoCl4 2- + 6H2O to demonstrate
- Kc is the ratio between reactants and products
- Kc ONLY change when you change temperature









