3.2 Periodic trends
Use page 8 and 9 of your data booklet!
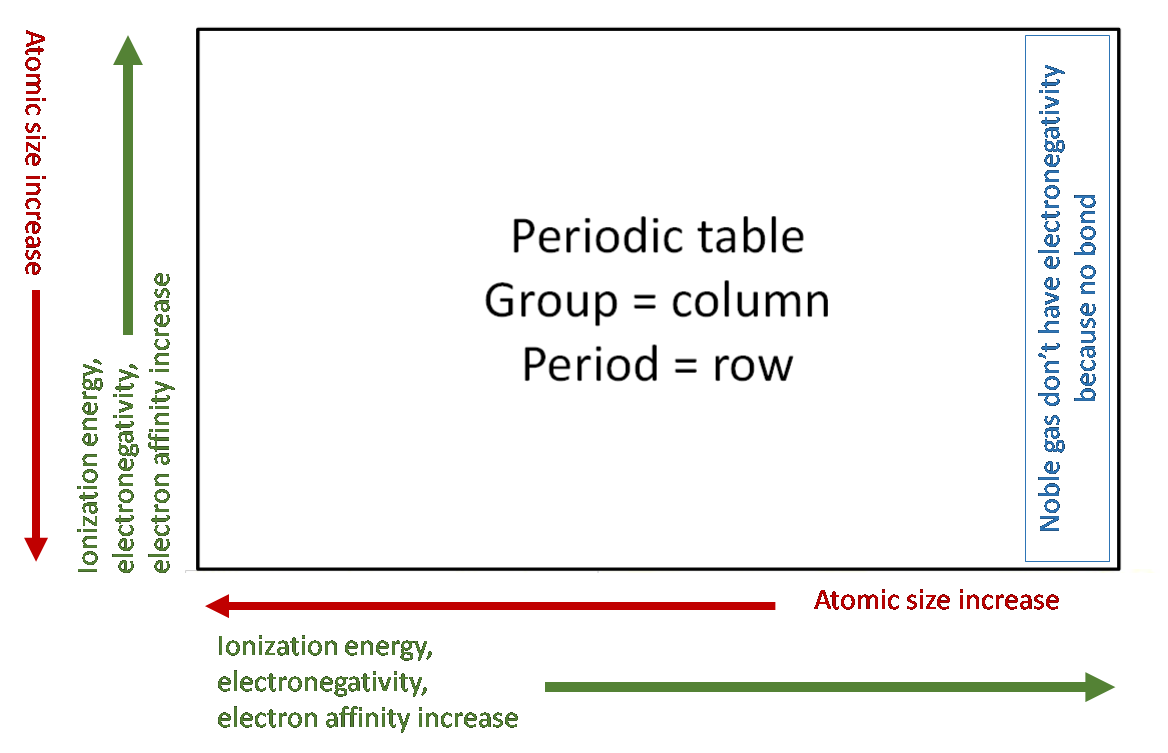
The characteristics of elements changes across a period and down a group
Key points to remember:
- Atomic radius (how big the atom is):
- More number of shells = bigger atom
- Same number of shells, more nuclear charge Z = smaller atom because electrons
experience larger effective nuclear force (ie. Electrons get pulled in more).
- First ionization energy (energy to remove first electron), electronegativity, and electron affinity all have opposite trend to atomic radius.
- What's the difference between electronegativity and electron affinity? Electronegativity = ability to attract electrons from within a covalent bond, electron affinity = energy give off when attract 1 mole of electrons to form 1 mole of negative ions. Also electron affinity is a negative number, ignore the sign when compare two values, Ex: -349 is larger EA than -325.
Note: in all IB definition of these terms, don't forget to say "in gaseous state" (it is one mark!!!)
Chemical properties of a few groups

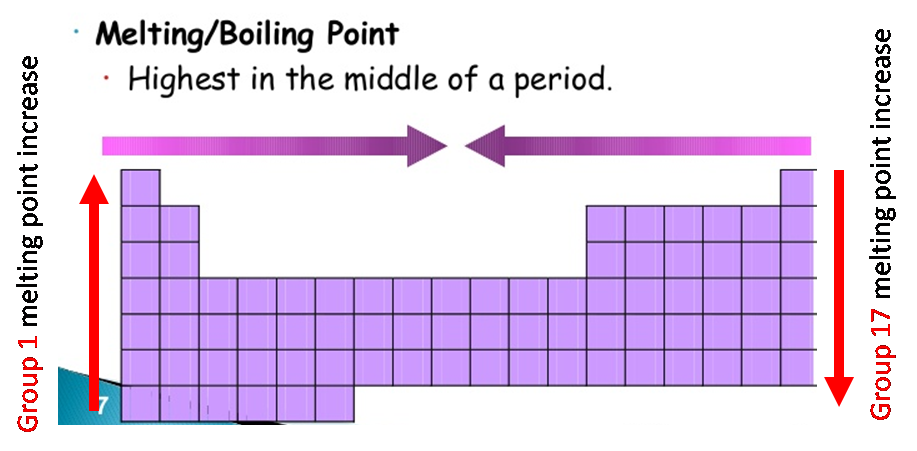
Melting points
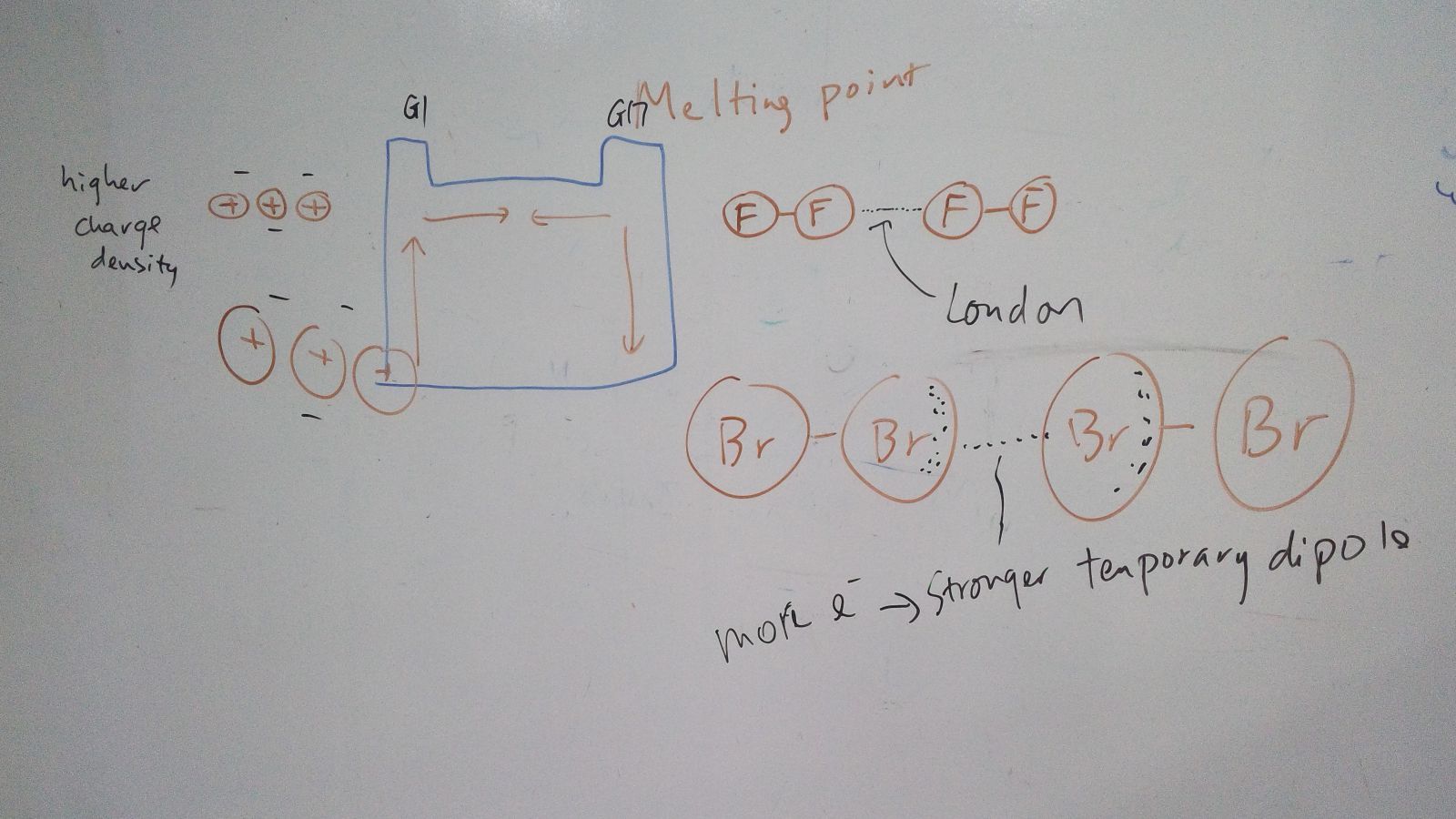
The melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements decrease going down the group. This is due to a decrease in the forces of attraction between the atom in solid state.
The melting and boiling points of the group 17 elements increase going down the group. This is due to a increase in the forces of attraction between the gas molecules (London force).