1.1.1 Matter
Atom, element, compound, and mixture
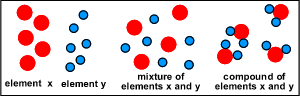
- Atom is the smallest unit of matter
- A type of atoms is called an element.
- Where there is two or more elements bind to each other, they are called a compound.
- When two elements or two compounds are mixed together, but they don't bond (link, interact) with each other, this is a mixture.
How is mixture different from compound?
Things (atoms or molecules) inside a mixture are not bonded to each others by ionic, covalent, or metallic bond. A compound must have atoms bonding to each other.
How are two types of mixtures differ?
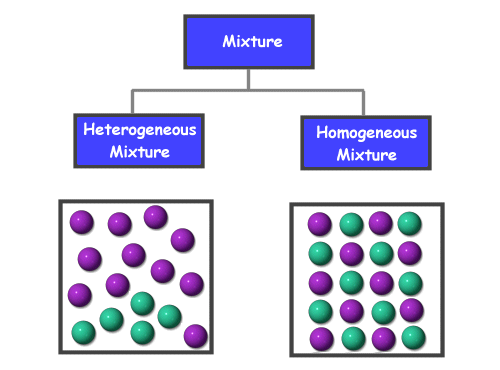
Examples:
Solutions (homogeneous) : salt and water
Alloys (homogeneous) : One example of an alloy is steel which is made from a mixture of iron and carbon
Suspensions (heterogeneous) : An example of a suspension is a mixture of water and sand
Colloids (heterogeneous): An example of a colloid is milk. Milk is a mixture of liquid butterfat globules dispersed and suspended in water.
How are mixtures get separated?
Solvation - dissolving a solute (the solid stuff) in a solvent (the liquid stuff, usually water)
Filtration - filter out the solute that wasn't dissolved in the solution
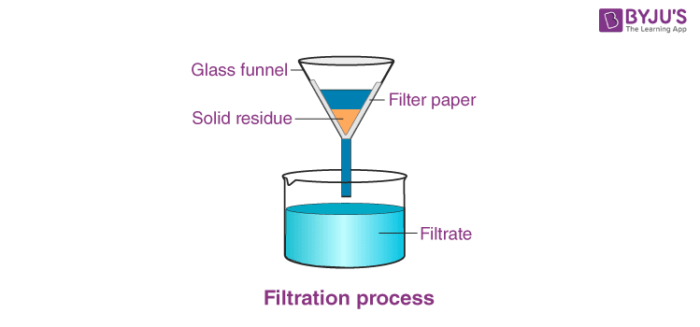
Recrystallization - reduce temperature so that the solute (pure substance) will "fall out" of the supersaturated (too full) solution
Evaporation - heat up to make the solvent (liquid part) turn into gas, leaving just the solute (pure substance)
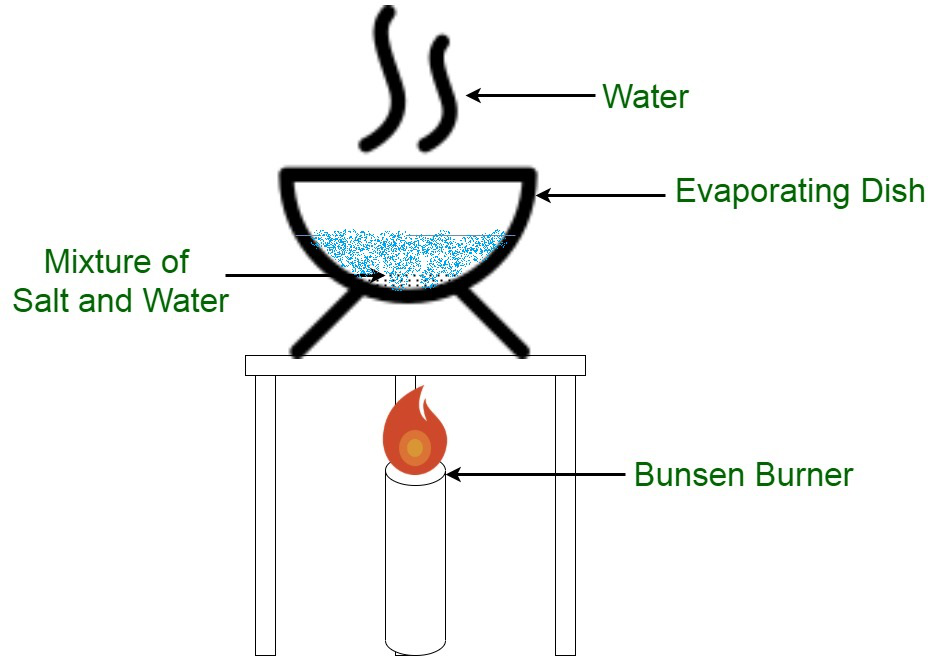
Usually solvation, filtration, and recrystallization/ or evaporation techniques are used together to separate the mixture
Distillation - separating the components of a liquid mixture through selective evaporation and condensation ie. a liquid evavoprate at lower temperature than the other liquid. Therefore, you can separate them.

Chromatography - separating components of a mixture using chromatography paper or resin ie. due to different properties of the components (mass, charge, solubility...), different parts of the mixture moves through the "special" paper or column of resin at different speed, thus you can separate them.










