2.1 The nuclear atom
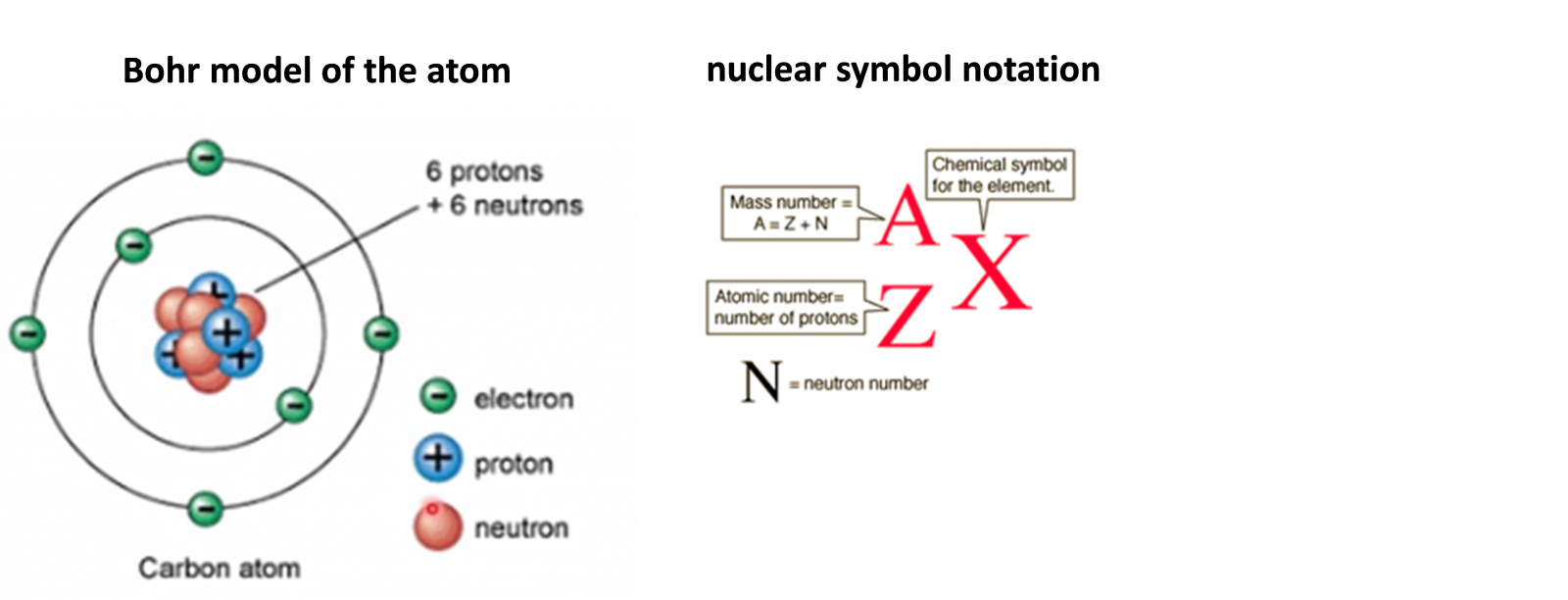
Z is also called nuclear charge = number of protons
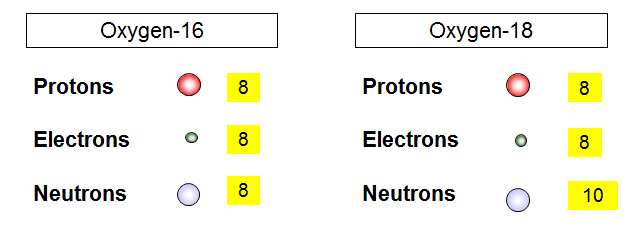
Isotopes = same element (same proton number) but different neutron number
= atoms with different mass
relative atomic mass (Ar) = average mass of an atom relative to C–12 having a mass of exactly 12
a.m.u = atomic mass unit
Example: oxygen has two isotopes 16O (99.8%), but about 0.2% is 18O. What is the relative atomic mass of oxygen?
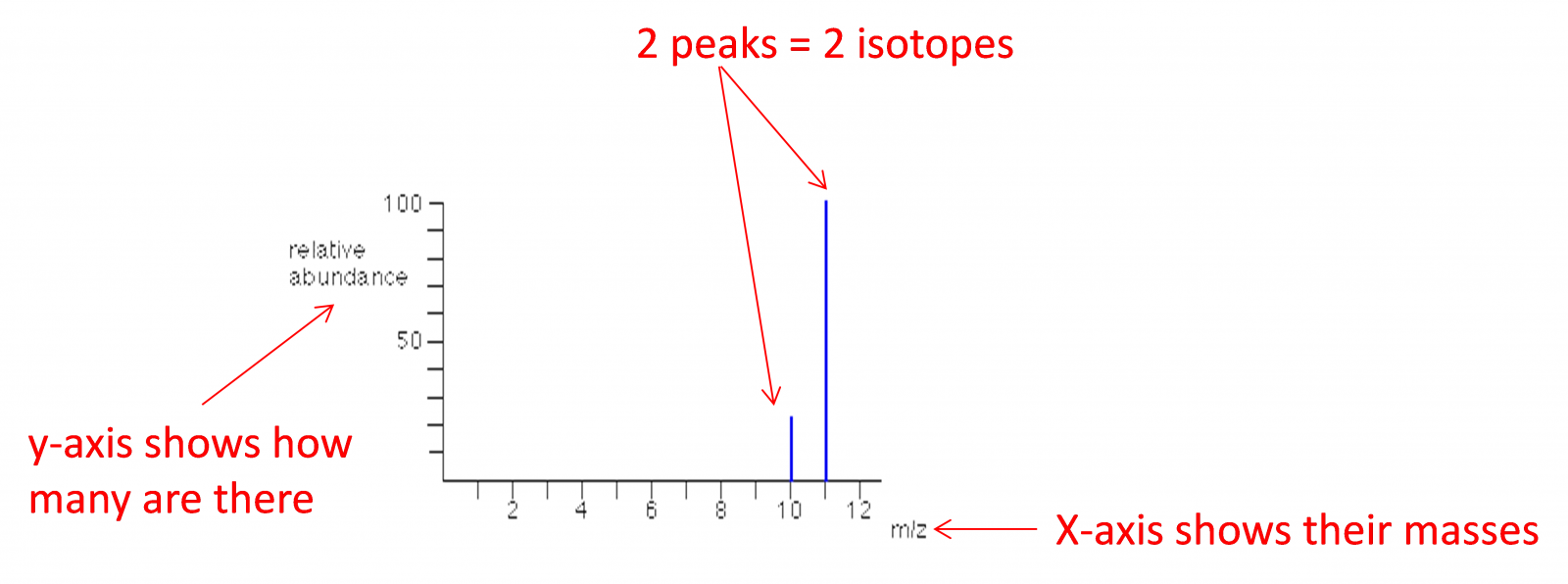
The mass spectrometer
This is a machine that can measure the atomic mass of an element and the composition of its isotopes. The operational details of the mass spec is not required.
(New Syllabus note)
SL need to calculate relative atomic masses from abundances of isotopes and vice versa
HL need to interpret mass spectra for identity and relative abundance