10.1c IUPAC rules of nomenclature (naming)

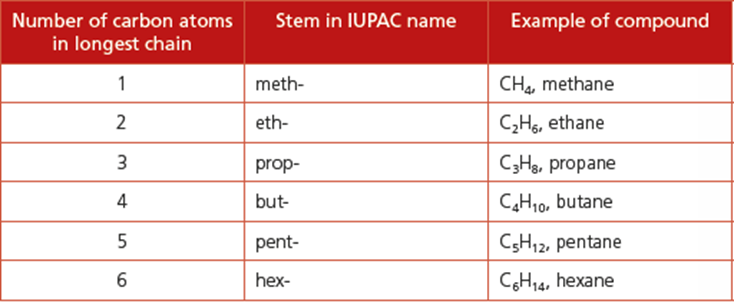
1. Identify the longest chain of carbon atoms
2. Identify the functional group
Suffix (the ending) adds to the name, which replaces the ‘-ane’ ending in the parent alkane
Note: you don't have to name Nitrogen containing functional group but you need to identify them
3. Position of the functional group
The position of the functional group is shown by a number between dashes inserted before the functional group ending
The number refers to the carbon atom to which the functional group is attached
4. Identify the side chains or substituent groups

The following nomenclature should be covered:
– non-cyclic alkanes and halogenoalkanes up to halohexanes.
– alkenes up to hexene and alkynes up to hexyne.
– compounds up to six carbon atoms (in the basic chain for nomenclature purposes) containing only one of the classes of functional groups: alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, halogenoalkanes, ketones, esters and carboxylic acids.









