10.2d Specific about alcohols
1. Combustion reaction: Alcohol burns in O2 (oxygen gas) to produce CO2 and H2O. Don’t forget to balance the equation.
CH3OH + 3/2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O
Or
2 CH3OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 4 H2O
2. Alcohols undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with acids (also called esterification or condensation)
3. Redox reactions
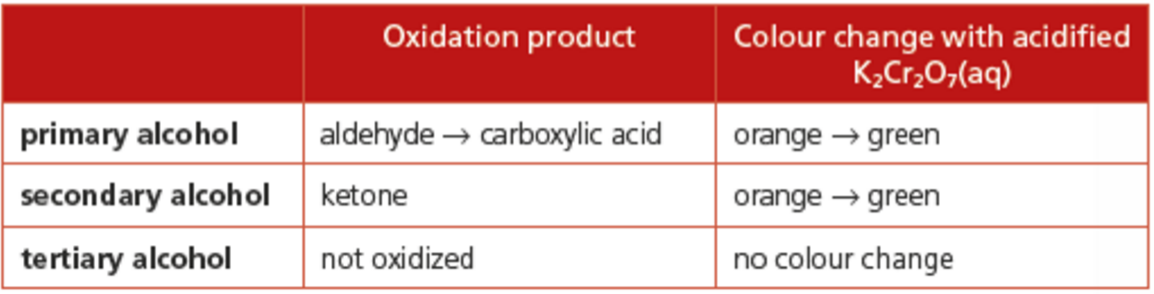
Primary alcohol can be oxidized in two steps. First step produces aldehyde. Second step produces carboxylic acid
Secondary alcohol can be oxidized only once to produce a keytone
Tertiary alcohol cannot be oxidized
During the oxidation, the orange dichromate ion is reduced to the green Cr3+ ion. This can be used to detect alcohols.
How to distinguish or to isolate the different types of alcohol?
Step 1: Add the alcohol to potassium dichromate(VI) solution acidified with dilute sulphuric acid. The tube would be warmed in a hot water bath.
Step 2: Isolate aldehyde and carboxylic acid using distillation and reflux









