9 Big picture about redox
Redox reaction is about the transfer of electron(s) from an atom (or ion) to another atom (or ion) that has more electron affinity, results in a change in charge
Example from Periodicity chapter
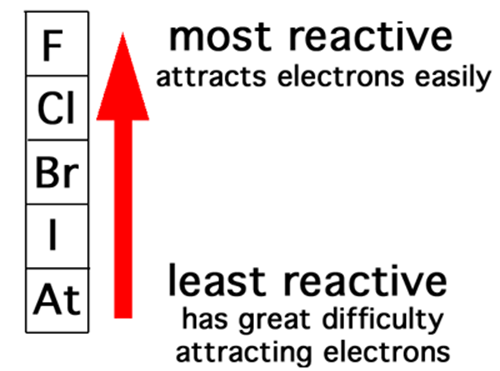
1. Cl2 (aq) + 2 Br- (aq) --> Br2 (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq)
This is a redox reaction
2. Cl2 (aq) + 2 F- (aq) --> NO REACTION
- Comparing the reactivity (based on ability to attract electron) of the two elements will tell you whether the reaction happens spontaneously or not
- If the reaction doesn't happen such as this example, you can force the electron transfer using external sources of energy. Ie. Electrical current produced by a battery
HL: Lewis acids accept and Lewis bases donate lone pair electrons, so is Lewis acid base reaction a redox reaction?
- NO. In Lewis acid base reaction, the lone pair electrons are usually shared as a covalent bond. There is NO CHANGE in the overall charge of the molecule/ atom so it is not redox reaction.
- Redox reaction usually involves ionic compounds.
- Acid + metal --> hydrogen gas + salt is redox where electron is transferred from metal to H+. Thus only metal that is more reactive than H+ can react with acid.









