9.1b Half equations
Full reaction: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Note that (s) means solid, (aq) means aqueous.
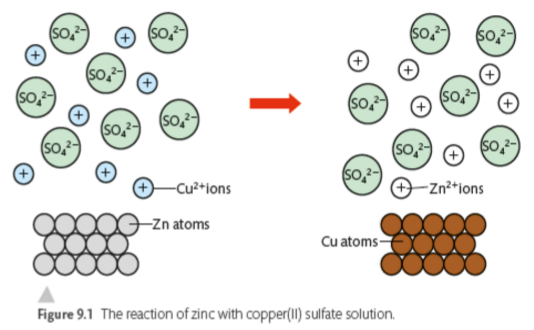
Essentially, solid Zn piece is dissolving while Cu2+ ions from the solution is depositing onto the electrode.
Half equations show oxidation and reduction process separately
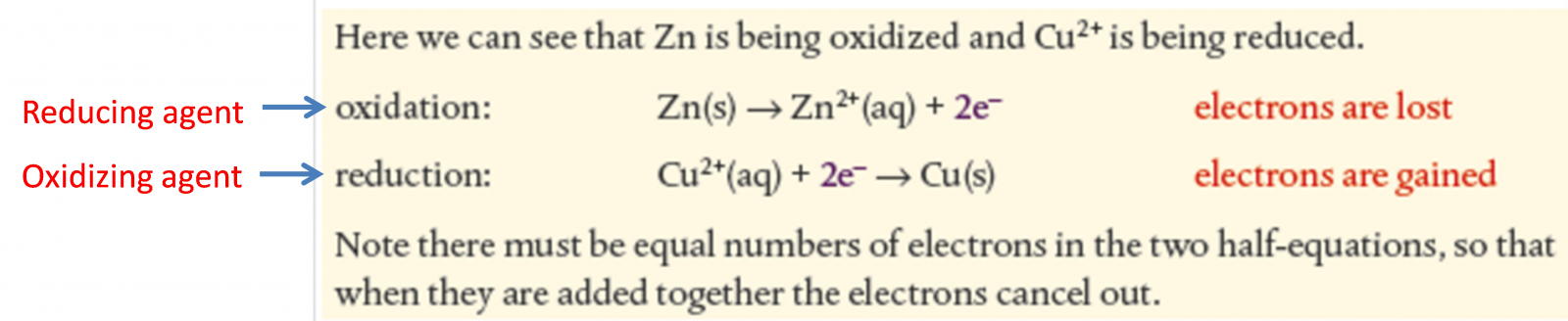
Spectator ions are not shown because they don't participate in reaction
Full equation
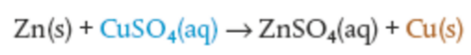
Net ionic equation
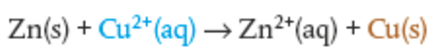
Spectator ions: SO42-









